In Mathematics, there are many curves. From a constant curve , to a linear one
, to a quadratic one
to …, you name it.
Now, imagine that there is a huge data set with some points (think ordered pairs for simplicity), but not all points are defined. Essentially, machine learning is all about coming up with a curve (based on a chosen model) by filling gaps.
Once we agree on the model we want to use (curve we want to represent), we start with some basic equation and then tweak its parameters until it perfectly matches the data set points. This process of tweaking (optimization) is called “learning”. To optimize, we associate a cost function (the error or delta between the values produced by the equation and the data set) and we need to find for which parameters this cost is minimal.
Gradient descent is one algorithm for finding the minimum of a function, and as such it represents the “learning” part in machine learning. I found this video by StatQuest, along with this video by 3Blue1Brown to be super simple explaining these concepts, and naturally, this article will be mostly based on them.
In this article I will assume some basic set theory, and also derivatives. Further, through example, we will:
- Define what the curve (model) should be
- Come up with a data set
- Do the “learning” using gradient descent
The most scholar example to start with is the Body Mass Index. We will assume that it follows a linear curve, of the form . Further, we will consider the following data set:
.
The question now is, which linear function (of the form ) “best” represents this data set? Is it maybe
, or
? There are infinite possibilities we can plug in for
but which values “best” represent the data set?
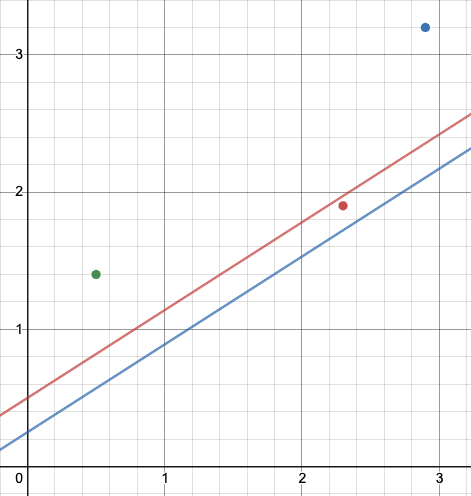
In order to answer that question, we must first define what “best” means. We need to find a way to measure it. We state that every curve will have a “cost” with respect to the data set. Cost is defined as how well the curve fits the data set.
Residual sum of squares is one type of a cost function. It is defined as , i.e. the sum of the square of every point from the data set subtracted from the function value.
Let’s try it for :
equals to around 1.053. On the other hand, for
we get 1.917. So
was a better choice in this case. The point is to find a function that has the least cost.
So we want to somehow optimize the cost function , and by optimize we mean to find the values
such that
produces minimum values. Note that
is simply the Residual sum of squares applied to our data set and the generic linear function. Once we find the values for
, we will just plug them in the linear equation
, and we can then use
to uncover the missing values.
Remember from high school that with derivatives we can find the critical point of a function, and in turn, determine the minimum/maximum points. To make our problem a little simpler we will assume , so our new cost function is now
. The next step is to calculate the derivative. For simplicity, with the help of an online calculator we determine that
. So to find a critical point, we just set the derivative to zero:
and we get that
. But in practice, it is not always easy to achieve this, as formulas get more complex. We turn to gradient descent.
The way the algorithm works is you start with a random point (value) for and calculate
. This will represent the value (not necessarily the minimal one) of the cost function at some random point. The algorithm needs to be repeatedly applied, subtracting the current value (
) from the derivative at this value (
) multiplied by the learning rate.
In other words, the algorithm is described by the formula , where
represents the array of values produced by the algorithm (
is usually some random number) and
represents the learning rate. The reason why this algorithm works is that we have
so with this, every iteration goes closer to the local minimum.
To see the algorithm in action, here’s an implementation in Python based on Wikipedia’s example:
next_x = 6 # We start the search at x=6
rate = 0.01 # Step size multiplier
precision = 0.00001 # Desired precision of result
max_iters = 10000 # Maximum number of iterations
iteration = 0 # Initial
dg = lambda a: (279*a - 287)/10 # Derivative function
assert(iteration < max_iters) # Precondition
while iteration < max_iters:
assert(callable(dg)) # Loop invariant I (before)
current_x = next_x
next_x = current_x - rate * dg(current_x)
if abs(next_x - current_x) <= precision: break
iteration += 1
assert(callable(dg)) # Loop invariant I' (after), I=I'
assert(iteration == max_iters # Postcondition
or abs(next_x - current_x) <= precision)
print("Minimum at %0.3f" % next_x) # 1.029
Now that we found out that , this means that
best represents our data set, and that we can use
to predict the missing values. For example, we can calculate
even though 7 was not in the original data set.
ML is all about gathering data, running simulations, and making the best decision with the information available.
Pretty cool, right? 🙂
Thanks for sharing such valuable content here. This is the information which I was searching for. Machine Learning is the learning of computer’s language which is very trending nowadays. To enhance skills in Machine Learning visit Universal Informatics to have best Machine Learning Training In Indore.
LikeLike